
Following the oral presentation at the European Lung Cancer Conference (ELCC), the poster at the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, and the full text publication in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine (latest IF: 102.642), the analytical data for CNS subgroup of the FURLONG study was rapidly published in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology (latest IF: 20.121) on August 4. It once again demonstrates the rigorous design, critical data and top-notch progress of the FURLONG study, and provides solid evidence-based support for the use of furmonertinib in the first-line treatment of NSCLC patients with EGFR mutation and CNS metastases.
More importantly, the frequent recognition of the pivotal study of furmonertinib by top international academic journals further strengthens the international academic position of furmonertinib and reflects the hardcore strength of independent research and development of Allist. The lights of China’s original innovative drugs shine on the international stage.
CNS subgroup data of FURLONG study
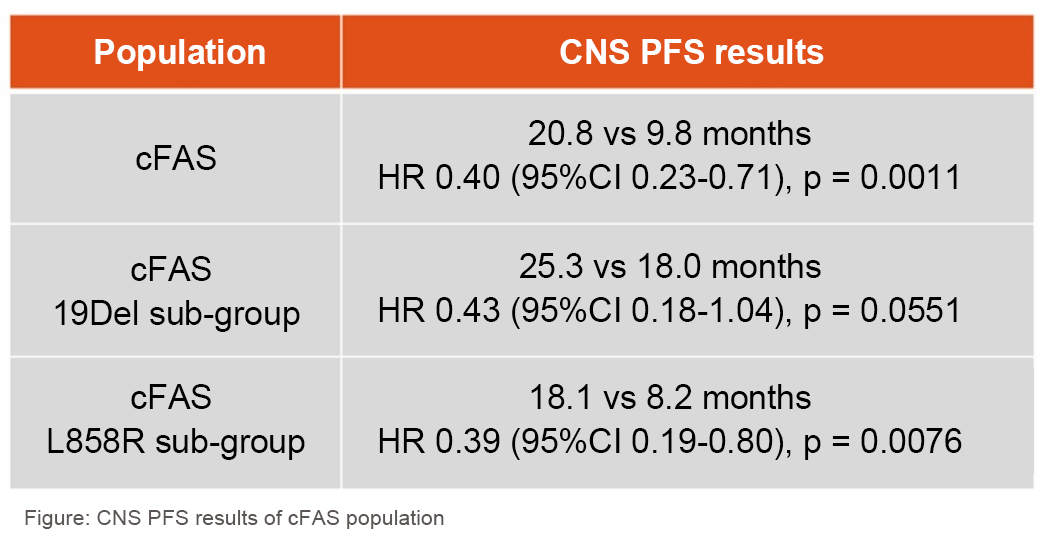
FURLONG is a phase III, national, multicenter, randomized, control, double-blind clinical study that enrolled 358 patients with EGFR-mutant locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC who were randomized to receive first-line treatment with either Furmonertinib or Gefitinib. A pre-planned CNS efficacy analysis was done in 133 patients with baseline brain metastases as assessed by Independent Review Committee (IRC) (cFAS), of which 60 patients with measurable brain metastases (cEFR) as assessed by IRC.
The results showed that CNS progression-free survival (PFS) in the cFAS population was significantly longer in the furmonertinib group than in the gefitinib group (CNS PFS, 20.8 versus 9.8 months, hazard ratio [HR] 0.40 [95% CI 0.23-0.71], p = 0.0011) and patients treated with furmonertinib had a reduced risk of CNS progression or death by up to 60%. In the cEFR set, furmonertinib significantly improved the CNS objective response rate (ORR) compared to Gefitinib (CNS ORR 91% versus 65%, odds ratio [OR] 6.82 [95% CI 1.23-37.67], p = 0.0277) and had a superior mean depth of response (62% versus 39%, mean difference 23%, p = 0.0011).
About the Journal of Thoracic Oncology
The Journal of Thoracic Oncology, the official journal of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC), is the primary educational and informational publication for topics relevant to the prevention, detection, diagnosis, and treatment of all thoracic malignancies, with the latest impact factor being 20.121.

